Lyman Alpha Galaxies
Young galaxies in the early universe can often be identified by
prominent emission of Lyman alpha photons. The Lyman alpha line
is the 2-1 transition
of neutral hydrogen. Galaxies with vigorous ongoing star
formation may be expected to show strong Lyman alpha emission lines,
because they contain young, massive, hot stars along with neutral
hydrogen gas. The hot stars emit copious amounts of ultraviolet
radiation, which ionizes the neutral hydrogen, breaking it into a free
electron and free proton. These particles later recombine to form
neutral hydrogen again. However this hydrogen is in an excited
state when formed, and as it relaxes back to the ground state, it emits
a series of line photons. 2/3 of the time, this series ends with
emission of a Lyman alpha photon. Lyman
alpha emission was first suggested as a signpost of galaxy formation in
by Partridge and Peebles in 1967.
The Large Area Lyman Alpha survey (LALA)
The Large Area Lyman Alpha survey is a project to identify and study
large samples of young galaxies in the early universe.
It began in 1998, with a proposal by Sangeeta
Malhotra and James Rhoads for
narrowband imaging on the Kitt Peak 4 meter Mayall telescope of the
National Optical Astronomy Observatory. Several other
collaborators have worked with us on various facets of the survey,
including Junxian Wang, Steven Finkelstein, Steve Dawson, Arjun Dey,
Daniel Stern, Buell
Jannuzi, Hyron Spinrad, Katarina Kovac, Emily Landes, Colin
Norman, Tim Heckman, and Rachel Somerville.
The LALA survey has two primary fields, in Bootes and in Cetus.
Both lie within broad band survey regions covered by the NOAO Deep Wide Field Survey.
The LALA survey has amassed samples of several hundred Lyman alpha
emitting
galaxies at redshift z=4.5, tens of galaxies at z=5.7, and one galaxy
at z=6.5.

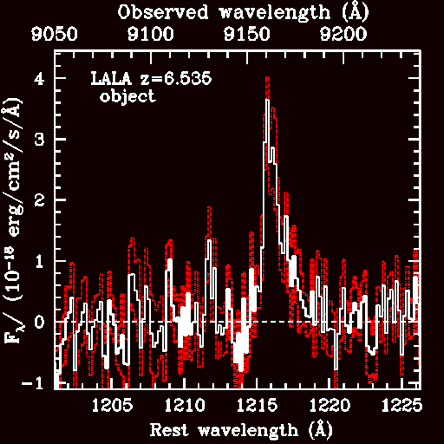
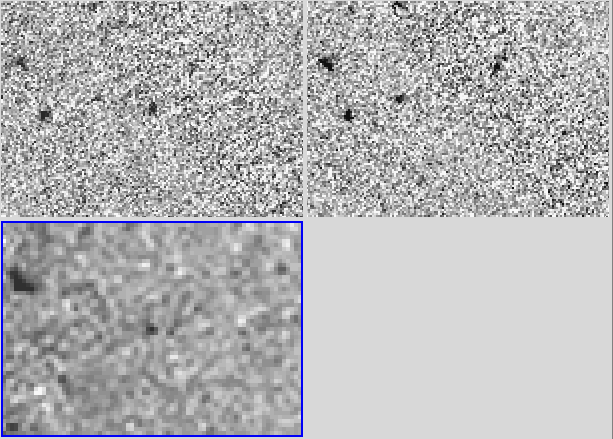
Panel 1 (left): Images of our redshift 6.535 galaxy in the i, z, and
NB918 filter, all from the Kitt Peak 4m Mayall telecope. Panel 2:
Gemini spectrum of the same object, showing a prominent, asymmetric
Lyman alpha line
on the right. Panel 3: Hubble Space Telescope images: z band (top
left), i band (top right), and H band (bottom left).
Lyman alpha publications:
The following chronological list covers most (but not all) of the Lyman
alpha related
papers that Sangeeta Malhotra and James Rhoads have worked on. A
good fraction of these are based on the Large Area Lyman Alpha survey
data, but again, not all.
- Rhoads, James E., Malhotra, Sangeeta, Dey, Arjun, Stern, Daniel,
Spinrad, Hyron, & Jannuzi, Buell T. 2000, Astrophysical Journal First Results
from the Large-Area Lyman Alpha Survey
- Rhoads, James E. & Malhotra, Sangeeta 2001, Astrophysical
Journal Lyα
Emitters at Redshift z = 5.7
- Malhotra, Sangeeta & Rhoads, James E. 2002, Astrophysical
Journal Large
Equivalent Width Lyα line Emission at z=4.5: Young Galaxies in a Young
Universe?
- Rhoads, James E., Dey, Arjun, Malhotra, Sangeeta, Stern, Daniel,
Spinrad, Hyron, Jannuzi, Buell T., Dawson, Steve, Brown, Michael J. I.,
& Landes, Emily 2003, Astronomical Journal Spectroscopic
Confirmation of Three Redshift z~5.7 Lyα Emitters from the Large-Area
Lyman Alpha Survey
- Malhotra, S., Wang, J. X., Rhoads, J. E., Heckman, T. M., &
Norman, C. A. 2003, Astrophysical Journal No
X-Ray-bright Type II Quasars among the Lyα Emitters
- Wang, J. X., Malhotra, S., Rhoads, J. E., Brown, M. J. I., Dey,
A.,
Heckman, T. M., Jannuzi, B. T., Norman, C. A., Tiede, G. P., &
Tozzi, P. 2004, Astronomical Journal The 172 ks
Chandra Exposure of the LALA Bootes Field: X-Ray Source Catalog
- Malhotra, Sangeeta & Rhoads, James E. 2004, Astrophysical
Journal Luminosity
Functions of Lyα Emitters at Redshifts z=6.5 and z=5.7: Evidence
against Reionization at z<=6.5
- Wang, J. X., Rhoads, J. E., Malhotra, S., Dawson, S., Stern, D.,
Dey, A., Heckman, T. M., Norman, C. A., & Spinrad, H. 2004,
Astrophysical Journal X-Ray
Nondetection of the Lyα Emitters at z~4.5
- Rhoads, James E., Xu, Chun, Dawson, Steve, Dey, Arjun, Malhotra,
Sangeeta, Wang, JunXian, Jannuzi, Buell T., Spinrad, Hyron, &
Stern, Daniel 2004, Astrophysical Journal A Luminous
Lyα-emitting Galaxy at Redshift z = 6.535: Discovery and Spectroscopic
Confirmation
- Dawson, Steve, Rhoads, James E., Malhotra, Sangeeta, Stern,
Daniel,
Dey, Arjun, Spinrad, Hyron, Jannuzi, Buell T., Wang, JunXian, &
Landes, Emily 2004, Astrophysical Journal Spectroscopic
Properties of the z ~ 4.5 Lyα Emitters
- Wang, J. X., Malhotra, S., & Rhoads, J. E. 2005,
Astrophysical Journal An
Overdensity of Lyα Emitters at Redshift z~5.7 near the Hubble Ultra
Deep Field
- Malhotra, Sangeeta & Rhoads, James E. 2006, Astrophysical
Journal The
Volume Fraction of Ionized Intergalactic Gas at Redshift z=6.5
- Kovač, Katarina, Somerville, Rachel S., Rhoads, James E.,
Malhotra,
Sangeeta, & Wang, JunXian 2007, Astrophysical Journal Clustering of
Lyα Emitters at z ~ 4.5
- Wang, J. X., Zheng, Z. Y., Malhotra, S., Finkelstein, S. L.,
Rhoads,
J. E., Norman, C. A., & Heckman, T. M. 2007, Astrophysical Journal Chandra X-Ray
Sources in the LALA Cetus Field
- Finkelstein, Steven L., Rhoads, James E., Malhotra, Sangeeta,
Pirzkal, Norbert, & Wang, Junxian 2007, Astrophysical Journal The Ages and
Masses of Lyα Galaxies at z ~ 4.5
- Dawson, Steve, Rhoads, James E., Malhotra, Sangeeta, Stern,
Daniel,
Wang, JunXian, Dey, Arjun, Spinrad, Hyron, & Jannuzi, Buell T.
2007, Astrophysical Journal A Luminosity
Function of Lyα-emitting Galaxies at z ~ 4.5
- Pirzkal, N., Malhotra, S., Rhoads, J. E., & Xu, C. 2007,
Astrophysical Journal Optical-to-Mid-Infrared
Observations of Lyα Galaxies at z~5 in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field: A
Young and Low-Mass Population


